50 Amazing Facts We Learned in the 2010s

Scientists, researchers, and even regular people going about their lives make amazing discoveries every day that change the way we see the world around us. That’s why it’s so thrilling to take a look back at how much we’ve learned just in the past decade. From animals to outer space to our own bodies, here are 50 amazing facts we learned in the 2010s.
1
More people die from selfies than shark attacks.

People are willing to do some pretty crazy things to capture a stunning selfie. And though some stunts are simply death-defying, others sadly result in serious injuries and even fatalities. In September 2015, Health.com found that while eight people had died following shark attacks since the beginning of that year, a total of twelve people had died due to dangerous selfie attempts. The deaths involved falling from precarious places while trying to get the perfect picture, as well as being hit by a train, being electrocuted, and even being gored while trying to take a selfie during the running of the bulls.
2
What we eat may have changed how we talk.

We were already aware that what we eat can have a major impact on our bodies. But in March 2019, Science published a study from the University of Zurich providing evidence that a change in human diets in the distant past actually altered how we speak, even adding new sounds to our speech. National Geographic explained that “the rise of agriculture thousands of years ago increased the odds that populations would start to use sounds such as f and v. The idea is that agriculture introduced a range of softer foods into human diets, which altered how humans’ teeth and jaws wore down with age in ways that made these sounds slightly easier to produce.”
3
We can “hear” the universe.

“A new era of astronomy has begun,” Space.com declared in 2017 when researchers discovered that they can “hear” the universe thanks to gravitational waves. In a revelation that Science deemed the Breakthrough of the Year, the waves were a result of two neutron stars colliding, something never before witnessed by scientists.
4
Cats recognize their own names but likely don’t care.

If you have a cat and a dog, you know your pup is much more likely to come running when they’re called. In a 2019 study published in Scientific Reports, researchers found that cats may recognize their own names, but they are also willing and able to ignore you when it suits them.
5
There’s a black that’s even darker than what was thought to be the blackest black.

Vantablack was once considered to be the “darkest man-made substance in the world,” according to CNN: “The original Vantablack is so black the human eye can’t quite decipher what it is seeing.” However, by the end of the 2010s, MIT engineers had developed something even darker. “Made from carbon nanotubes, the new [still unnamed] coating is … 10 times blacker than anything that has previously been reported,” said MIT News.
6
Dinosaurs may have shed their skin in small pieces instead of all at once like modern reptiles.

Anyone with pet snakes or lizards knows that these animals shed their skin in one long piece. Scientists once believed that dinosaurs got rid of their skin just like modern reptiles, but they now believe the ancient animals may have shed smaller pieces—what the BBC deemed “dinosaur dandruff.”
7
“Shamrock-colored” puppies exist.

Dogs come in a range of shapes and sizes, all of which are cute. They also come in various colors—even green! In 2017 and 2019, “shamrock-colored” puppies were born. The greenish coloring, which eventually fades, is thought to be due to “the bile pigment biliverdin in the womb,” according to IFL Science. “Biliverdin is a greenish color and can be found in bile, bruises, the placenta of dogs, and many other biological phenomena. Scientists have even found biliverdin in the shells of 6-million-year-old dinosaur eggs.”
8
A duck-billed dinosaur lived in Japan.

Kamuysaurus japonicus was officially welcomed into the dinosaur family just this September thanks to the discovery in northern Japan of a nearly complete skeleton among marine deposits that date back a whopping 72 million years. After being examined, it turned out that the bones belonged to a previously unknown “herbivorous hadrosaurid [duck-billed]” dinosaur.
9
A “third eye” allows sea turtles to sense when the seasons change.

You might think that a turtle’s shell is its snazziest feature, but their “third eye” is pretty darn incredible as well. In 2014, scientists published findings that addressed the pink spot that’s located on the heads of leatherback sea turtles. The researchers discovered that in this area “the layers of bone and cartilage were remarkably thinner than in other areas of the skull,” according to Science. “This thin region of the skull allows the passage of light through to an area of the brain, called the pineal gland, that acts as [a] biological clock, regulating night-day cycles and seasonal patterns of behavior.” Therefore, the spot acts like a “skylight,” which lets the turtles “sense the subtle changes in sunlight that accompany changing seasons, signaling them to return south when autumn approaches.”
10
One-third of sushi is not what you think it is.
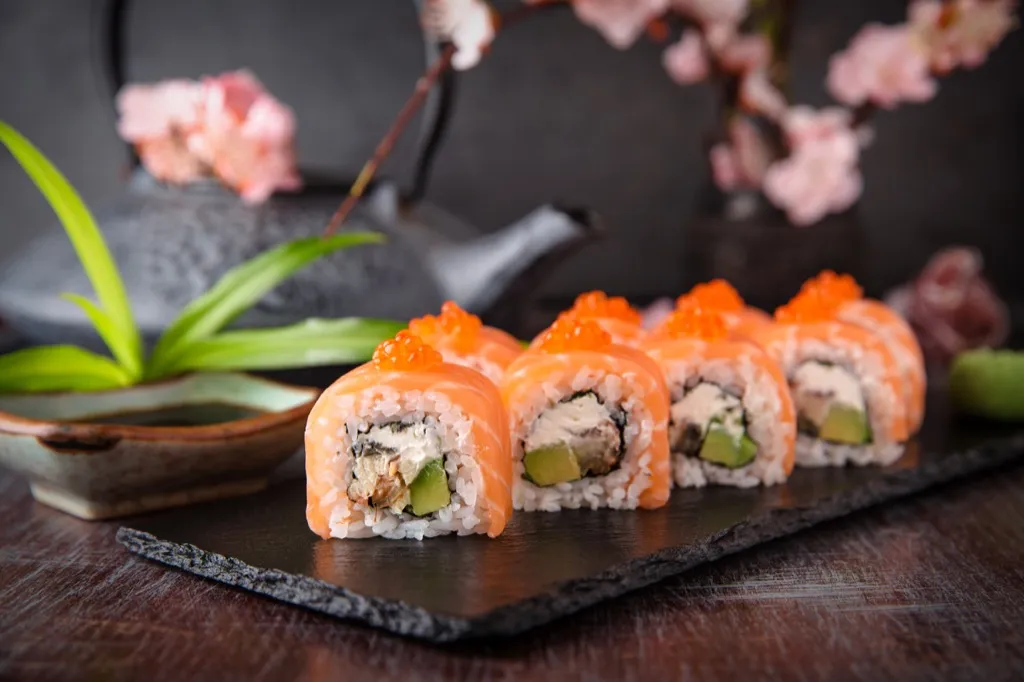

The next time you purchase fish, you might want to be sure you’re actually getting what you asked for—whether that’s salmon, tuna, or halibut. A study conducted between 2010 and 2012 by the international conservation organization Oceana found that “consumers are often given insufficient, confusing or misleading information about the fish they purchase.” The massive investigation, which involved DNA testing samples of fish from retail outlets in 21 different states, “found that one-third, or 33 percent, of the 1,215 seafood samples were mislabeled, according to U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) guidelines.”
11
Bees stop buzzing during total solar eclipses.
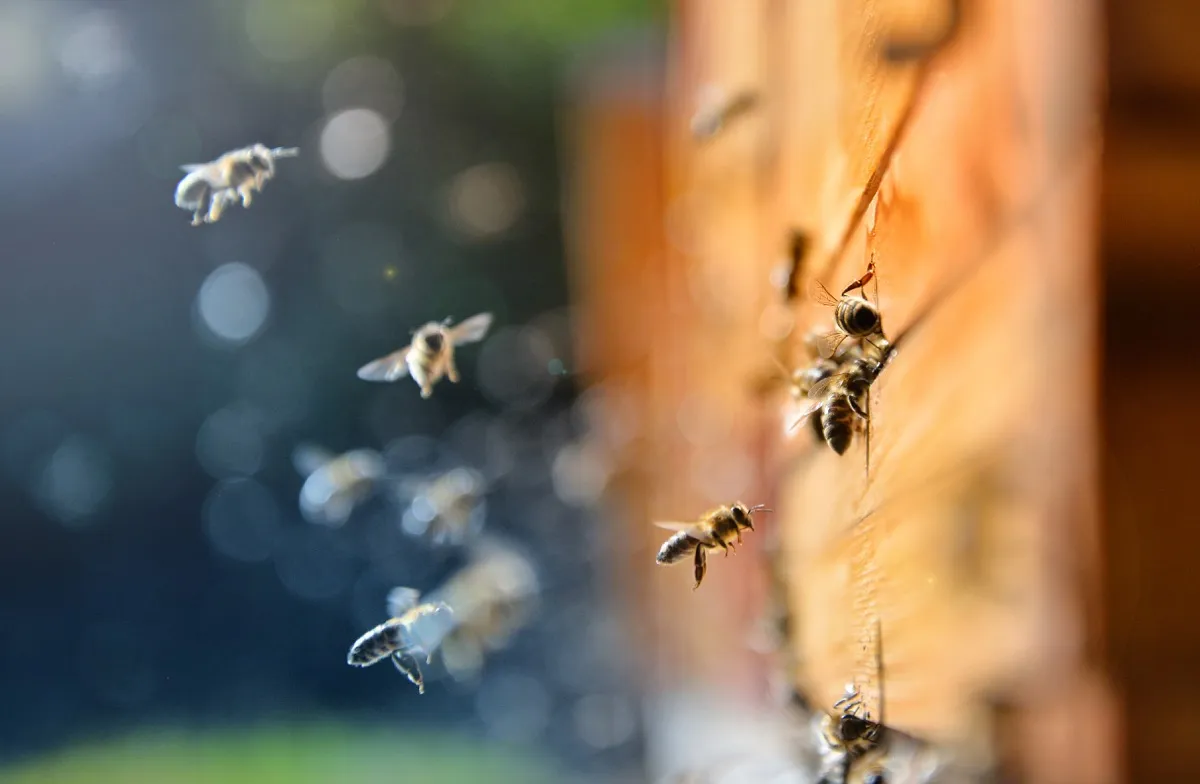

Many people drop what they’re doing to observe a solar eclipse, and it turns out that bees also pause during the sun-related phenomenon. Researchers from the University of Missouri used mini microphones to observe the tiny creatures during a 2017 eclipse and discovered that the bees stopped buzzing as the moon blocked the sunlight and created darkness down on Earth. “It was like someone turned out the lights and bees stopped flying,” said ecologist Candace Galen, lead author of the 2018 study, which was published in the Annals of the Entomological Society of America. “It was abrupt, it wasn’t gradual. It was like falling off a cliff, that abrupt.”
12
Human bodies can move for more than a year after death.
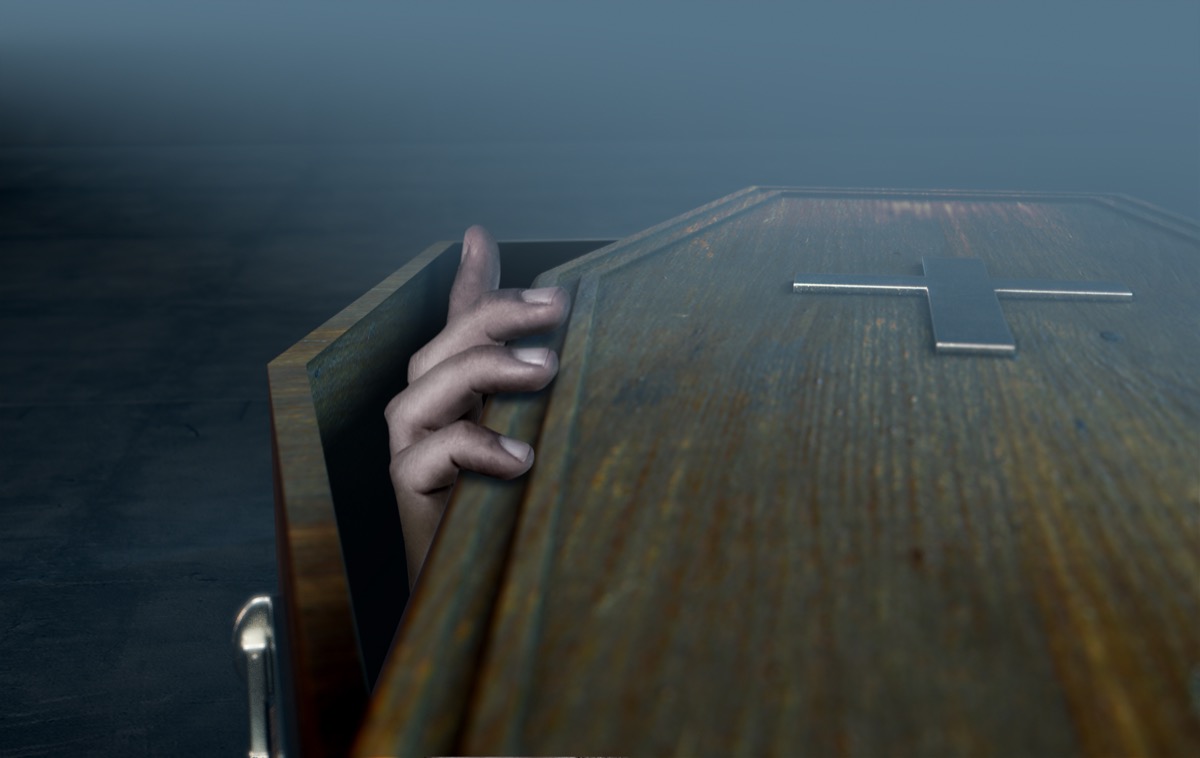

Strange things happen to human bodies after death, and that includes the fact that they can continue to move for more than a year after a person has died. In 2019, Australian researchers used time-lapse cameras and “found … that the arms [of corpses] were significantly moving, so that arms that started off down beside the body ended up out to the side of the body,” according to Central Queensland University’s Alyson Wilson. She explained, “We think the movements relate to the process of decomposition, as the body mummifies and the ligaments dry out.”
13
Venus probably used to be a habitable planet.
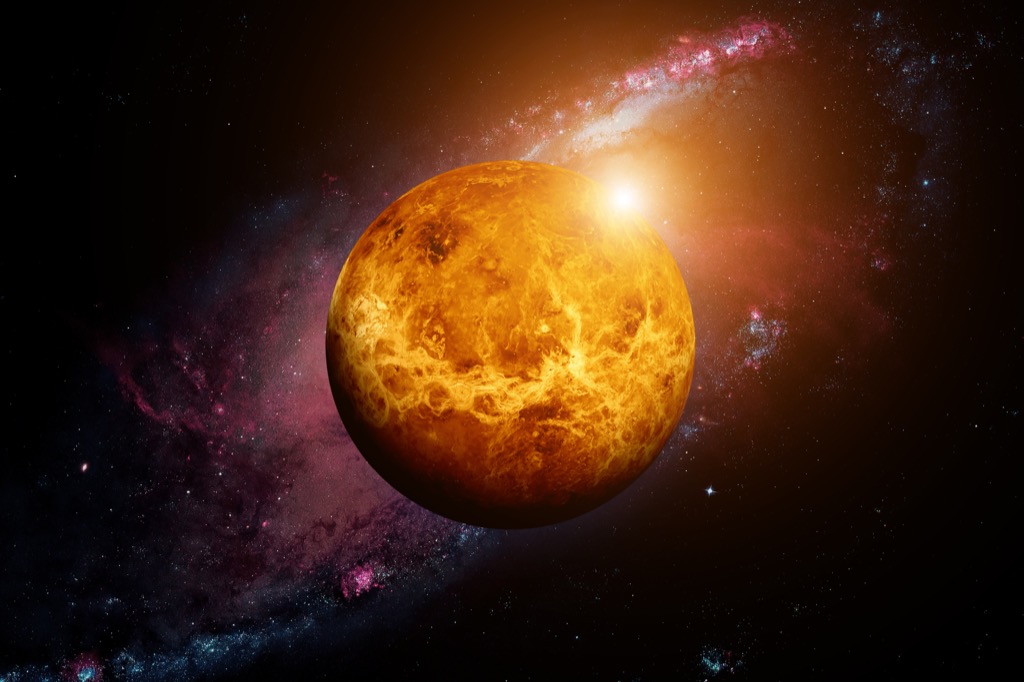

Venus is certainly not a place you’d want to live due to blazing temperatures and nasty sulfuric acid clouds. However, it turns out that it might not always have been so incredibly inhospitable. According to Smithsonian, “Simulations show the planet could have maintained moderate temperatures and liquid water until 700 million years ago.” In fact, it was “downright Earth-like for 2 to 3 billion years.”
14
Your eardrums move when you move your eyes.

Your eardrums don’t have anything to do with your sense of sight, as far as we know. That’s why it was so surprising when a 2018 study in PNAS revealed that our eardrums move when we move our eyes.
15
The world’s most intense natural color comes from an African fruit.

Pollia condensata is a small blue fruit that grows in African forests in countries like Ethiopia, Mozambique, and Tanzania. While it can’t be eaten, Smithsonian reported that a 2012 study “determined that the fruit’s tissue is more intensely colored than any previously studied biological tissue—reflecting 30 percent of light, as compared to a silver mirror, making it more intense than even the renowned color of a Morpho butterfly’s wings.”
16
Tasting sugar helps boost self-control.

It’s no secret that sugar gives you a rush of energy, but it turns out that it might also help self-control. For a 2012 study published in the Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, participants who were engaging in certain tasks were given a glucose mouth rinse when they felt themselves waning. As a result, they “performed significantly better on a subsequent self-control task.”
17
Humans remember 5,000 faces on average.

If you were in a room of thousands of people, how many do you think you’d be able to remember? According to findings published in Proceedings B in 2018, you’d likely be able to recall the faces of around 5,000 people, which is the average number that humans can remember.
18
Plants can learn and remember.

We already knew that plants are surprisingly dangerous and have genius ways of protecting themselves. But in 2014, we learned that plants are even more clever than we realized. When biologists from Australia and Italy tested plants in the same way they would test animals, they proved that “Mimosa pudica—an exotic herb native to South America and Central America—can learn and remember just as well as it would be expected of animals,” Sci-News.com explained.
19
Our galaxy is probably filled with thousands of tiny black holes.

When you think of a black hole, you might picture a massive void in space. But for years, astronomers suspected that thousands of smaller versions were floating around our galaxy. And in 2018, scientists published evidence to Nature backing up this theory. According to their research, “as many as 20,000 black holes are predicted to settle into the central parsec of the Galaxy.”
20
Grapes catch fire in the microwave.

It’s hard to imagine why you’d want to put a grape in a microwave, but if you happen to try heating one up, you should know that it will catch fire—like in this experiment conducted in 2011. In 2019, the PNAS journal explained that “by expanding this phenomenon to whole spherical dimers of various grape-sized fruit and hydrogel water beads, we demonstrate that the formation of plasma is due to electromagnetic hotspots arising from the cooperative interaction of Mie resonances in the individual spheres.” Or more simply: It’s the plasma created in the wet grape pieces that turn it into a sparking snack.
21
Commuting can be good for relationships.

Making your way to and from work tends to be a tedious task, especially if it’s a long trip. But if you and your significant other share a commute, it might actually make your relationship stronger. A 2012 study in the Journal of Experimental Social Psychology looked at two different surveys—one in the U.S. and the other in Hong Kong—that both found “partners’ satisfaction with their relationship was greater when they traveled to work in the same direction than when they traveled in different directions.” What made it even more interesting was that this stayed true even when “the partners left for work at … different times.”
22
Fonts that are harder to read might be more convincing.

Whatever font you choose likely matches not only your taste but also your purpose. That’s why, if you’re writing something that you hope will be convincing, you should use an odd font, which was reported to be more likely to win someone over. A 2013 study in the Journal of Experimental Social Psychology showed that when readers have to slow down to decipher each word, it forces them to spend more time thinking about each fact and argument.
23
Some spiders make milk for their babies.
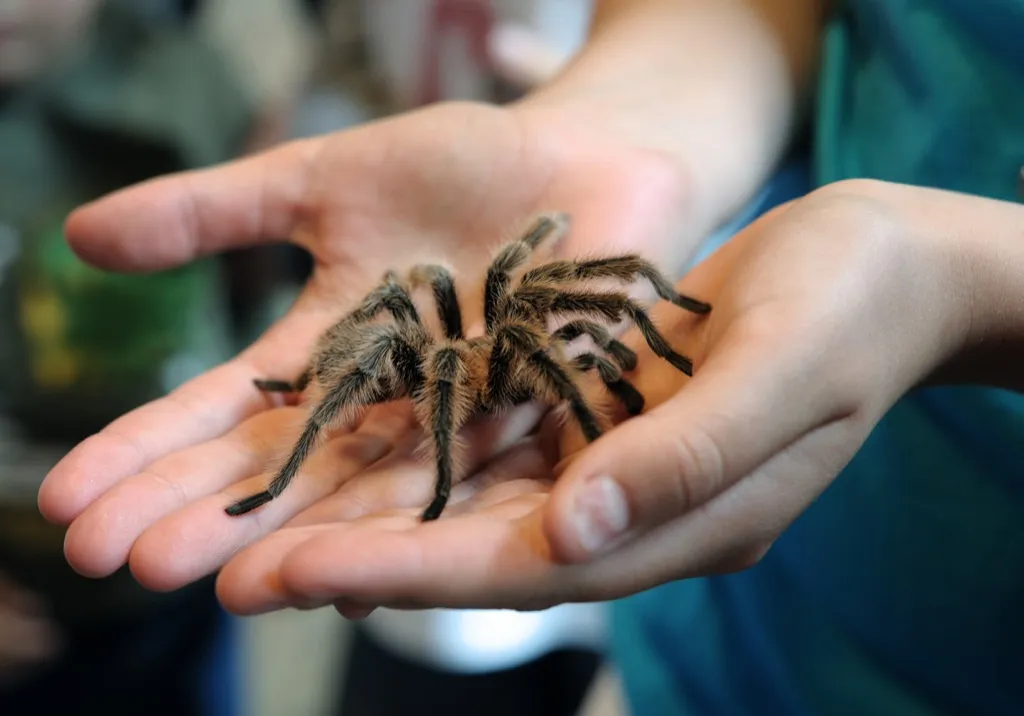

Thanks to their arguably creepy appearance, spiders don’t have the best reputation, despite being master web-makers and fly-eaters. But maybe this amazing spider fact researchers discovered in 2018 will sway the haters. A study published in the journal Science explained the details of “milk provisioning in a jumping spider, which compares functionally and behaviorally to lactation in mammals.” Baby spiders—or spiderlings—“ingest nutritious milk droplets” that their mothers produce and secrete.
24
Giraffes with dark spots are more dominant and solitary than giraffes with light spots.
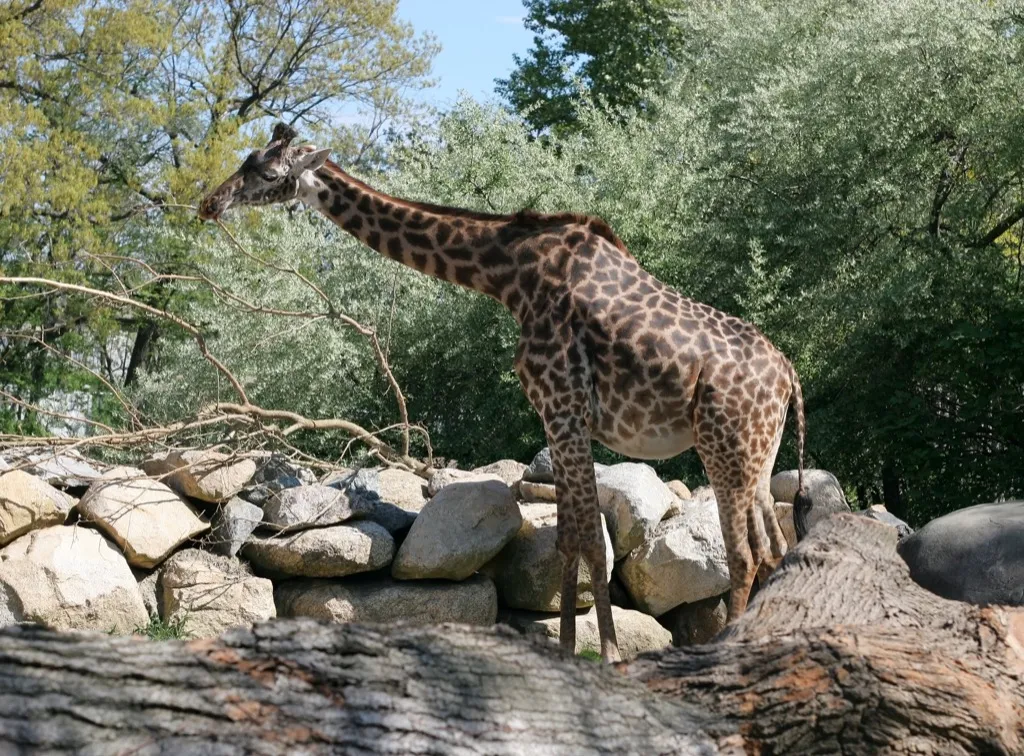

It turns out a giraffe’s spots can say a lot about them—just refer this 2019 study in Animal Behaviour for the details. While it was once believed that giraffes with light spots were more dominant than their dark-spotted pals, the opposite is now thought to be true. Giraffes with dark spots are also thought to be more solitary animals than those with light spots.
25
The world is running out of sand.
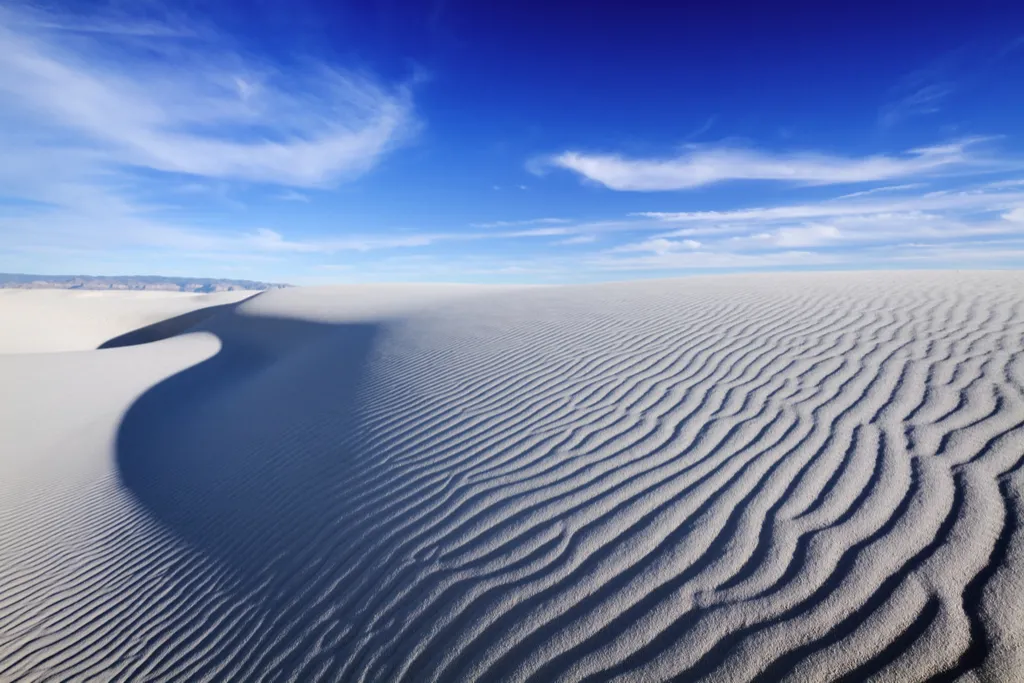

You might want to enjoy the beach before it’s too late, because the world is running out of sand. We’re using too much! “In most regions, sand is a common-pool resource, i.e., a resource that is open to all because access can be limited only at high cost,” a 2017 study in Science noted. Basically, sand is free and easy to access. Because of this, “people may selfishly extract [it] without considering long-term consequences, eventually leading to overexploitation or degradation.”
26
There’s an extremely rare flower that only lives on two cliffs in Spain.

If you want to spot a truly unique plant, you’ll have to plan a trip to one of two adjacent cliffs in Spain which are the only spots where the rare Borderea chouardii flower grows. The PLOS One journal published findings on the flower in 2012, noting that some of the plants are believed to be over 300 years old. But if you happen to find one way up in the Pyrenees, be aware that they’re endangered—so look, but don’t touch!
27
Looking up to a superhero can have a positive effect on a man’s self-image.
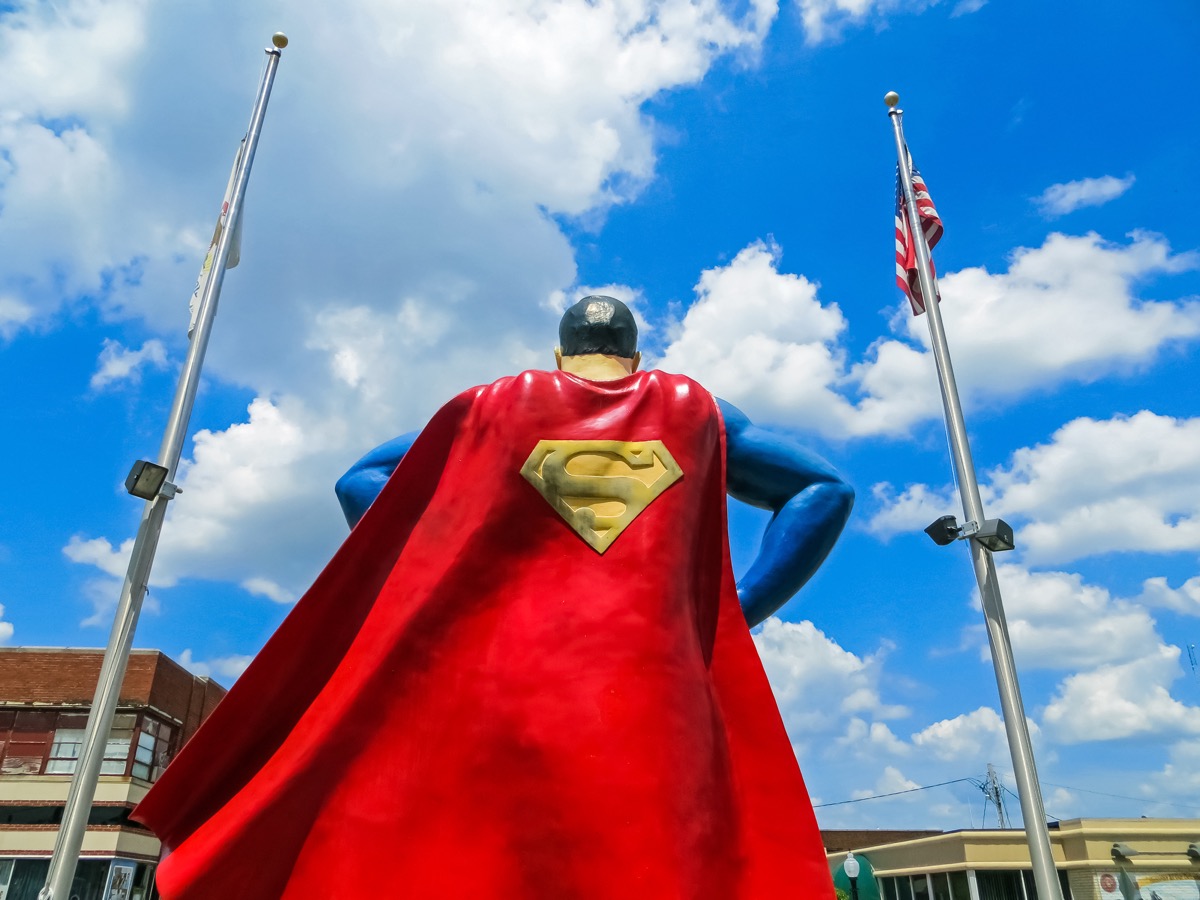

Do you have a favorite superhero? Whoever gets your justice-seeking mojo going, you should know that they’re likely having a positive influence on the way you see yourself. A study from 2012—published the following year in the Journal of Experimental Social Psychology—revealed that men who look up to superheroes tend to take on the fictional character’s confidence when it comes to their own body image.
28
Man-eating Nile crocodiles live in Florida.

Just how scary is the wildlife in Florida? In 2016, DNA tests published in the journal Herpetological Conservation and Biology confirmed that man-eating Nile crocodiles had made their way into the state’s waters. Yikes!
29
Pluto has “floating mountains.”
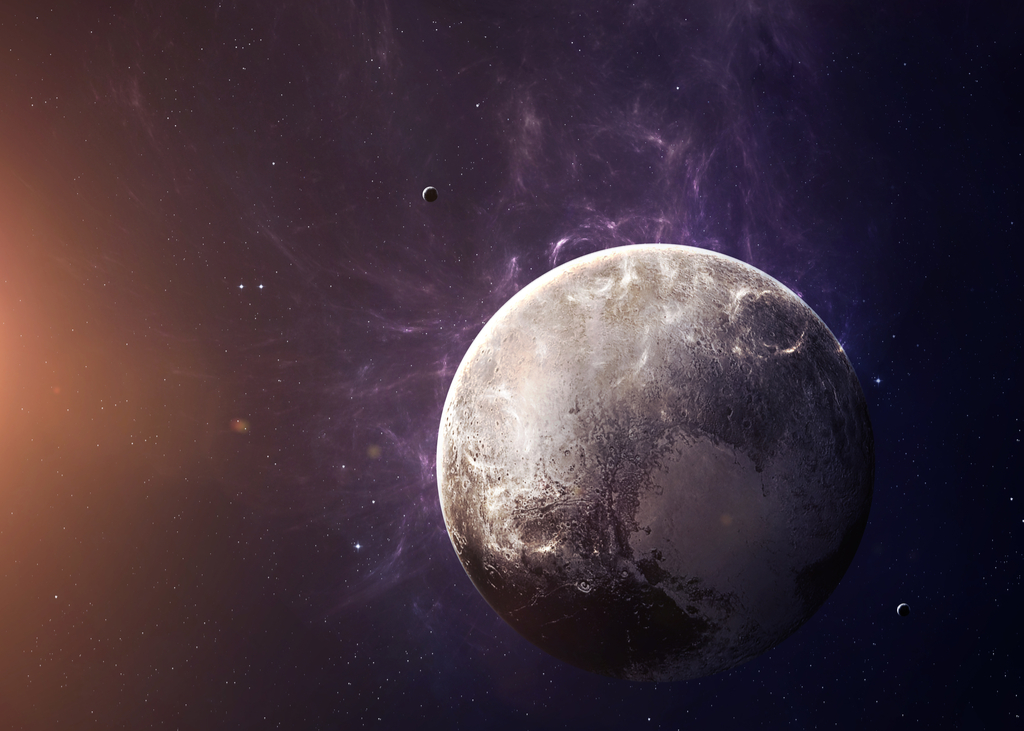

On July 14, 2015, NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft flew by Pluto and gave us a close-up look at the small planet. Among other amazing discoveries to come out of the trip, scientists were able to identify what National Geographic described as “enormous, floating mountains made of water ice.”
30
There are sharks that look like tiny sperm whales.

Mollisquama mississippiensis, discovered in the Gulf of Mexico back in 2010, was deemed a “pocket shark” in 2015, but further studies revealed it to be a new species in 2019. Only 5.5 inches long, the tiny shark doesn’t look like a great white or hammerhead, but instead resembles a mini sperm whale.
31
Cheetahs don’t overheat while running.
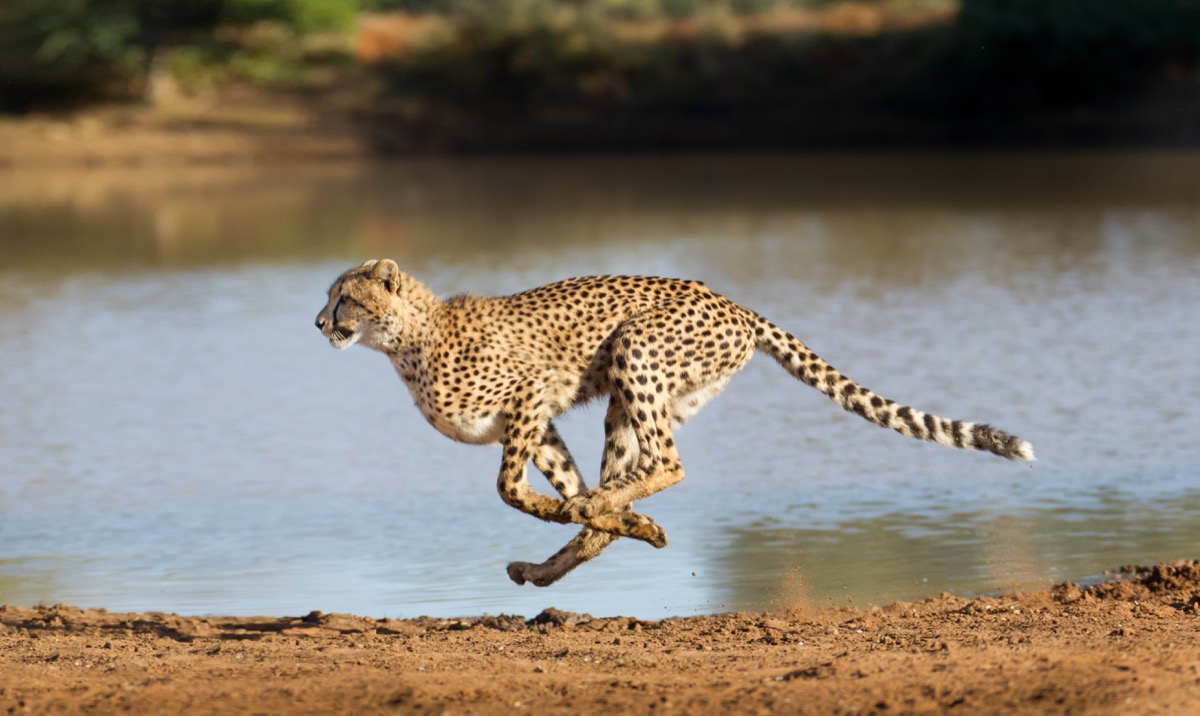

Cheetahs are among the fastest creatures in the world and can reach speeds of around 60 miles an hour while chasing their prey, although some can be even speedier. However, the swift creatures can only sustain their top speed for a short period of time, something scientists once thought was because cheetahs simply got too hot to continue. In 2013, that was proven false. “Cheetah do not abandon hunts because they overheat,” explained a study published in Biology Letters. Scientists remotely measured the body temperature of cheetahs in action, and found that their inner temperatures weren’t the problem at all.
32
Scientists found seven Earth-sized planets orbiting one star.

It was certainly an incredible discovery when, in 2017, astronomers found a group of Earth-sized planets circling a distant star. What made the find even more amazing was the fact that each planet might be able to support life. Study co-author Brice-Olivier Demory, a professor at the Center for Space and Habitability at the University of Bern in Switzerland, said that if we’re “looking for life elsewhere, this system is probably our best bet as of today.”
33
Humans have an organ called an interstitium that’s about 20 percent of our body weight.
If you were asked to point to the general area of your body where your interstitium resides, would you be able to find it? Probably not since it’s an organ that was only identified in 2018, by way of a study published in Scientific Reports. “Scientists discovered the new organ, which consists of fluid-filled spaces, in the body’s connective tissue, including in the skin’s dermis,” said Live Science. So where is the interstitium? Well, pretty much everywhere. “These fluid-filled spaces were discovered in connective tissues all over the body, including below the skin’s surface; lining the digestive tract, lungs and urinary systems; and surrounding muscles.”
34
A psychoactive parasitic fungus can make a cicada’s butt fall off.
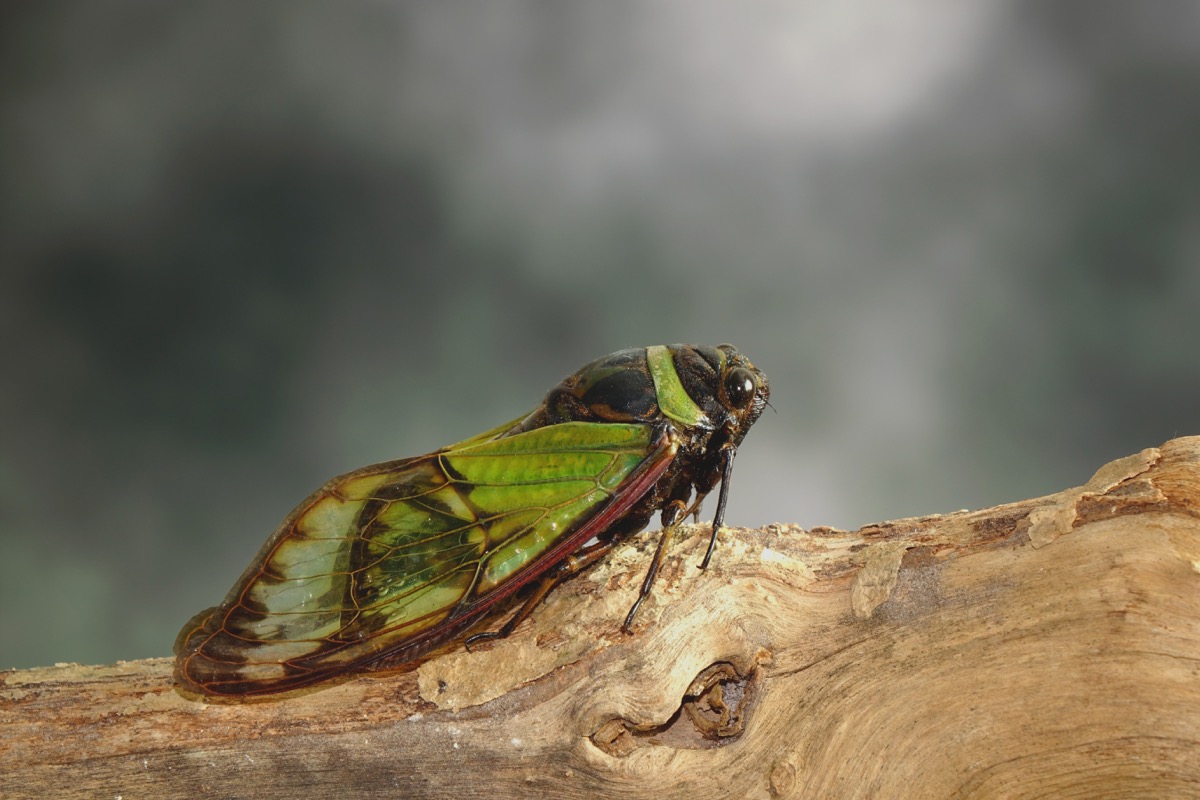

When cicadas come across the spores of the Massospora fungus, a psychoactive plant, it causes their backsides to harden and fall off. That was old news, but a 2018 study published on bioRxiv revealed that it’s the trippy qualities of the fungus that make cicadas apathetic to the sudden loss. “A week after these encounters, the hard panels of the cicadas’ abdomens slough off, revealing a strange white ‘plug.’ That’s the fungus, which has grown throughout the insect, consumed its organs, and converted the rear third of its body into a mass of spores,” The Atlantic explained. Thanks to the psychoactive nature of the fungus, the “de-derriered insects go about their business as if nothing unusual has happened.”
35
Researchers found evidence of liquid water on Mars.

The chance of life existing on another planet is much more likely if there’s water to be found. That’s why it was so exciting when, in 2015, scientists tracked down evidence of “liquid water flows” on Mars, which increases “the odds that life could exist on the Red Planet.” Georgia Institute of Technology in Atlanta’s Lujendra Ojha, the lead author of the study which presented the evidence, explained, “The presence of liquid water on Mars’ present-day surface therefore points to environment[s] that are more habitable than previously thought.”
36
Bacteria can conduct electricity.

Despite their small size, bacteria are quite powerful in their own way—they can even conduct electricity. A 2012 study published in the journal Nature revealed that filamentous bacteria can carry electrons over a distance of centimeters. That may not sound like a lot, but it’s quite an accomplishment for such a tiny organism.
37
Two genes may fuel your dreams.
Genes are pretty powerful, too. In fact, scientists identified two genes—Chrm 1 and Chrm 3—that may be partially responsible for your dreams, as seen in a 2018 study in Cell Reports. Mammals need to experience rapid eye movement (REM) in order to dream and, according to Live Science, without these two genes, “mammals would not experience … REM sleep.”
38
Half of all food is thrown away.
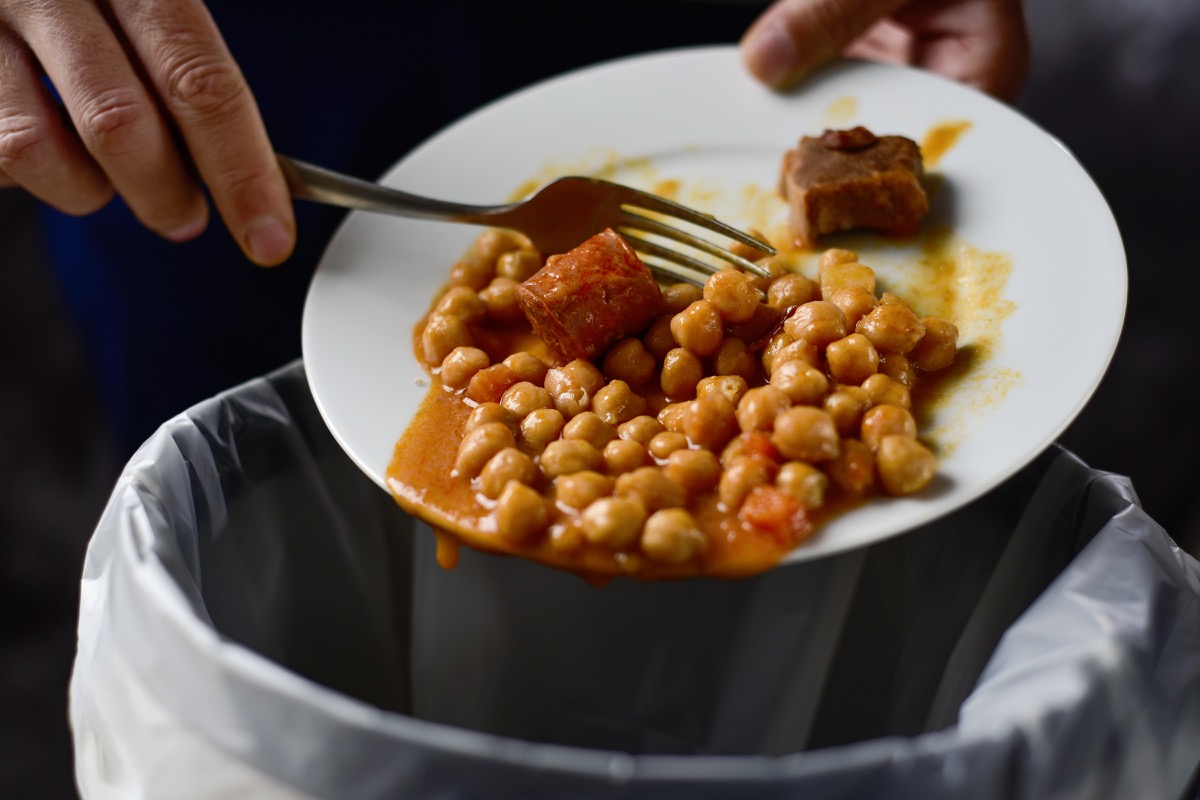

If you hate to waste food, it may frustrate you to know that anywhere between 30 and 50 percent of the food that we produce—or around 1.2 to 2 billion tons—never gets eaten, according to a 2013 report from the Institution of Mechanical Engineers (IME). “The amount of food wasted and lost around the world is staggering,” Tim Fox, head of energy and environment at IME, told The Huffington Post at the time. He noted, “This is food that could be used to feed the world’s growing population—as well as those in hunger today … It is also an unnecessary waste of the land, water, and energy resources that were used in the production, processing, and distribution of this food.”
39
An aging ape experiences a midlife crisis just like humans.
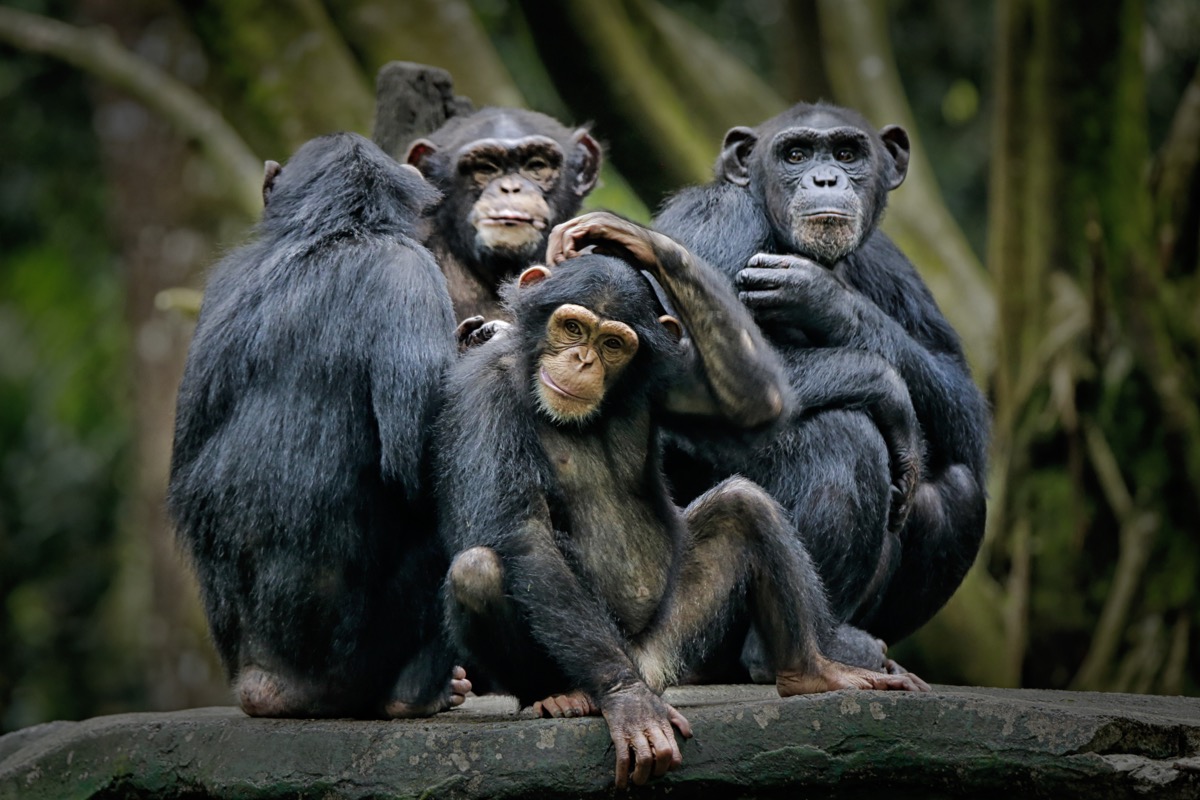

Humans and apes share many similarities, including the fact that they both experience what we would call a midlife crisis. In a 2012 study published in PNAS, researchers explained that when it comes to humans, “a large range of well-being measures, including happiness and mental health, [falls] in midlife, and rises again in old age.” They added that the “reasons for this U-shape are still unclear.” However, what they do know is that “a similar U-shape exists in 508 great apes” whose well-being was monitored during a study of their behavior.
40
There are at least 100 billion planets in our galaxy alone.

From our perspective down on Earth, it may appear as if space is filled with stars and only dotted with a few planets here and there. But in 2013, astronomers at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena came up with a rather staggering number to contradict that. “There are at least 100 billion planets in the galaxy, just our galaxy,” said John Johnson, assistant professor of planetary astronomy at Caltech. Clearly impressed by the findings in the study he co-authored, he stated, “That’s mind-boggling.”
41
Some catfish have learned how to kill pigeons.
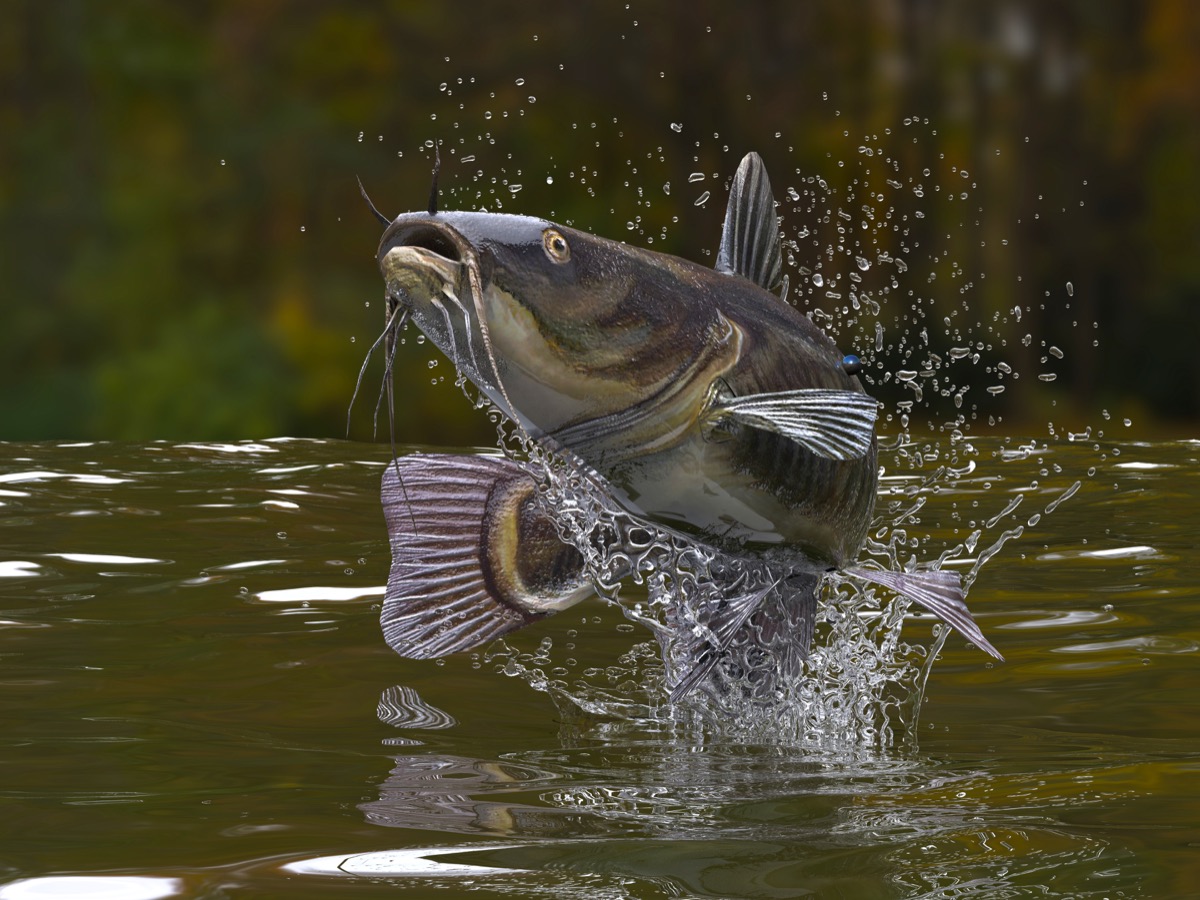

When it comes to birds and fish, you probably think of the birds as the hunters and fish as the prey. But in some circumstances, the opposite is true. In 2012, Discover Magazine reported that European catfish have learned how to kill pigeons. The predatory swimmers launch themselves out of the water to target birds on the shore. If the fish successfully nabs a bird, the hunter wiggles its way back into the water where it can devour its meal.
42
Pop music is getting sadder.

You’re not just imagining it: Pop music is getting sadder. A 2012 study published in the journal Psychology of Aesthetics, Creativity, and the Arts found “that popular music [has become] more sad-sounding over time.” Psychologist E. Glenn Schellenberg and sociologist Christian von Scheve said, “As the lyrics of popular music became more self-focused and negative over time, the music itself became sadder-sounding and more emotionally ambiguous.”
43
NASA found a possible energy source for life on Saturn’s icy moon.

Most of us think about possible life in outer space existing on another planet, but what about moons? In 2017, NASA’s Cassini spacecraft found a potential energy source for living beings on Enceladus, Saturn’s moon. An icy place, Enceladus has a subsurface ocean that may feature chemical reactions like the kind that help lifeforms survive around Earth’s own deep-sea hydrothermal vents.
44
Close friends really do think alike.

If you and your besties seem to be on the same wavelength, there may be a scientific explanation behind that. Carolyn Parkinson, an assistant professor of psychology at the University of California, Los Angeles, was the lead author in a 2018 study published in Nature Communications that compared the brain activity of close friends. Parkinson explained in a statement that the “results suggest that friends process the world around them in exceptionally similar ways.”
45
Australians have been eating a kind of fish unknown to science.

When a fisherman contacted Queensland Museum fish expert Jeff Johnson, he was hoping Johnson could help him identify a fish he’d caught but never seen before. Johnson didn’t have an answer, but he was willing to track down the same kind of fish at an area market. After doing tests, it was determined that the Australian locals had been eating a species of fish that was previously unknown to science.
46
Children with authoritarian parents are more likely to be Republicans as adults.

Strict parents tend to produce right-wing adults. Pacific Standard broke down the findings of the 2012 study published in Psychological Science, reporting that researchers were able to establish “a link between a mother’s attitude toward parenting and the political ideology her child eventually adopts. In short, authoritarian parents are more prone to produce conservatives, while those who gave their kids more latitude are more likely to produce liberals.”
47
A star was discovered to be two massive blue stars merging into one.

Located in the constellation of the Giraffe (seriously), which lies 13,000 light-years from Earth, there’s a star cluster known as MY Camelopardalis. According to a study published in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2014 was the year astronomers realized that MY Camelopardalis was not one star but two massive blue stars merging into one.
48
Video games may help fight depression.

Playing video games may actually help fight depression, according to a 2018 study published in Frontiers in Psychology: “Results show that the fast paced action video game employed in the present study improved … performance and may reduce rumination and enhance subjective cognitive ability.”
49
A body found under a parking lot was King Richard III.
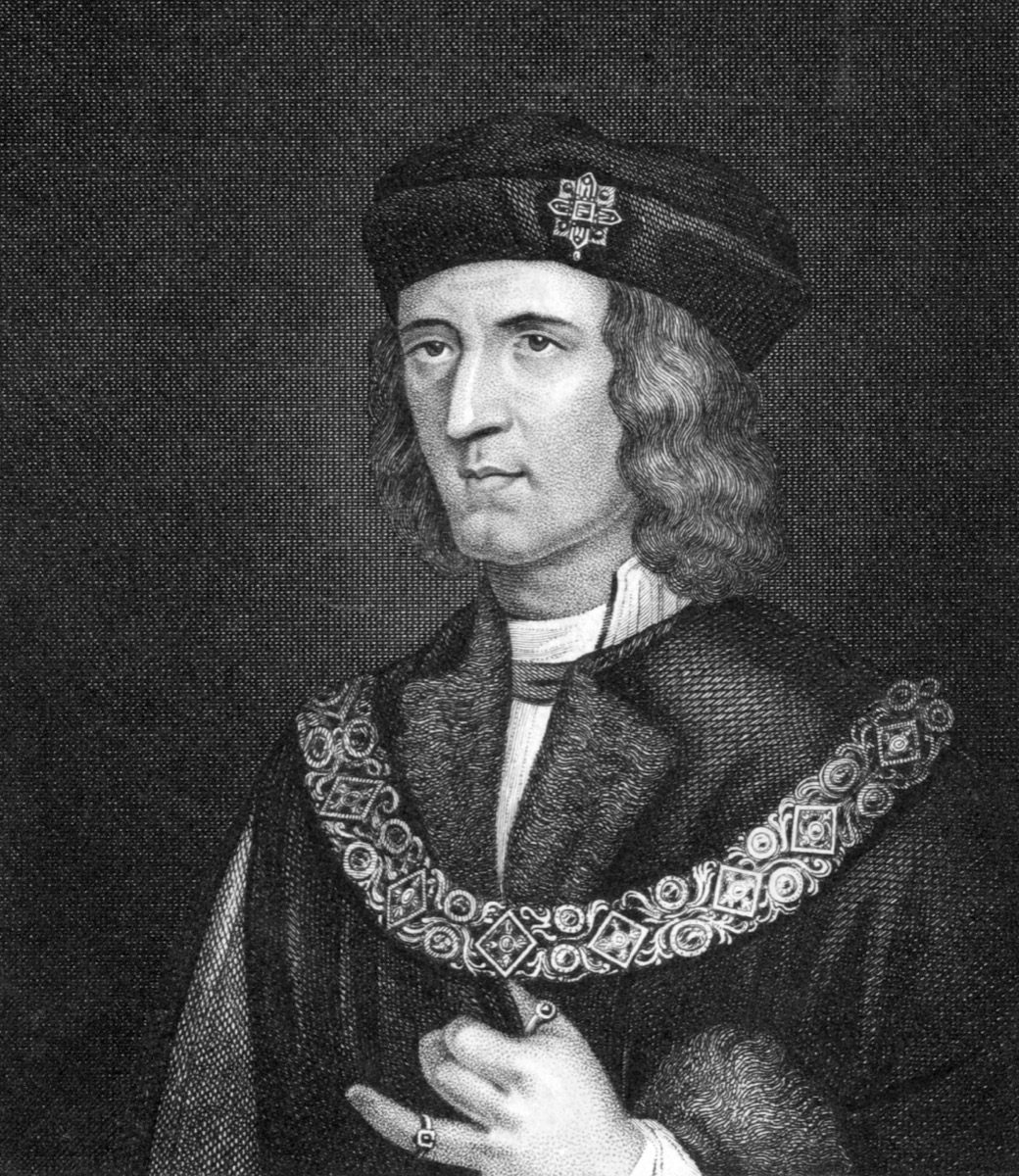

After years of research and speculation, it was determined in 2013 that the skeleton uncovered in an excavation of a parking lot in England belonged to King Richard III. It turned out his body had gone through a rather undignified journey following his death during the Battle of Bosworth Field in 1485.
50
The Knights Templar had secret tunnels in Israel.
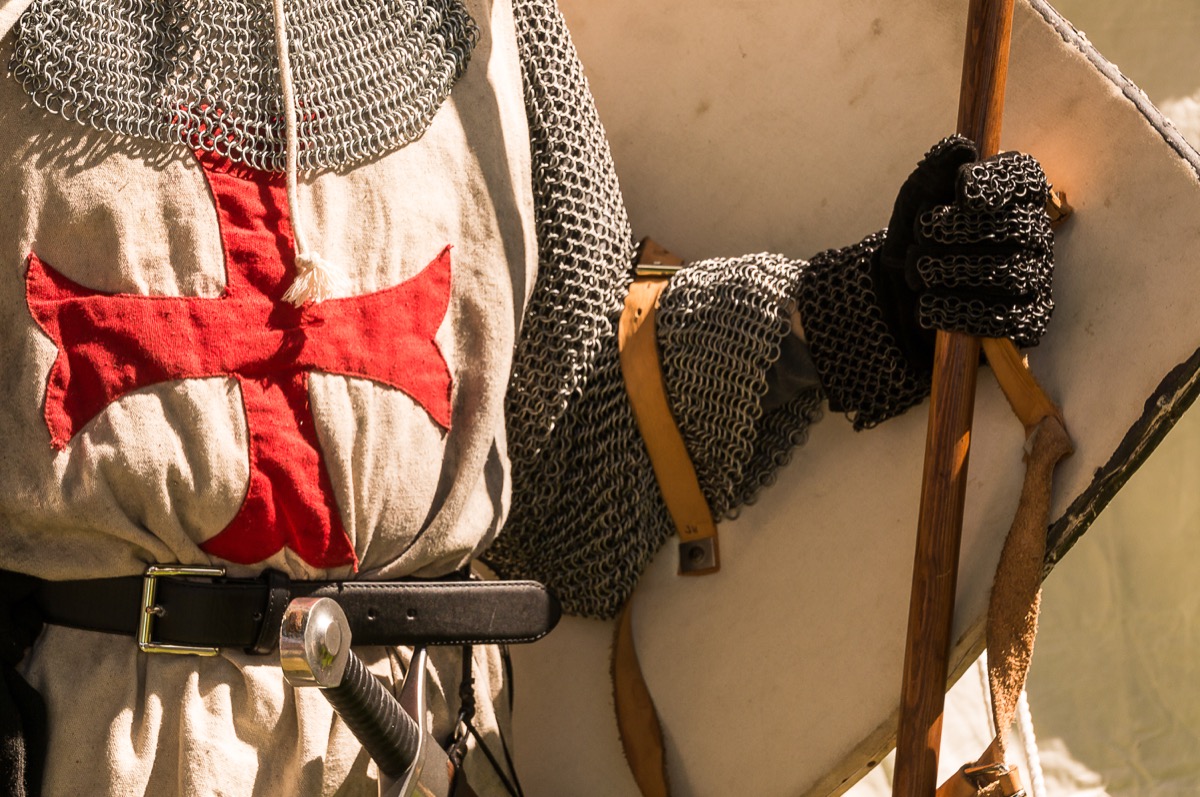

The Catholic military order of the Knights Templar was famous for guarding the Holy Grail, but they were also powerful men with the resources to make their way across great distances to fulfill their quests. Even knowing that, it was still a thrill to discover a series of secret subterranean tunnels in Israel that were once used by the Templars when they flooded the Holy Land for their Crusades.