16 Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms to Watch Out For, According to Doctors

Some vitamin deficiencies are more common than others, and few are more prevalent than vitamin D deficiency. In fact, according to the Cleveland Clinic, 35 percent of all American adults have this particular health problem. Among seniors, the numbers are far more staggering: 78 percent of people over 65 have low vitamin D levels, one 2007 study says. Getting too little vitamin D can have a serious impact on your health, but the good news is that it’s detectable, preventable, and treatable. Read on to find out which symptoms signal a vitamin D deficiency and what you can do about it, according to doctors.
RELATED: 7 Low Magnesium Symptoms to Watch Out For, According to Doctors.
What Is Vitamin D?

Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that your body needs for optimal bone health and a range of other functions. Your body produces vitamin D after being exposed to the sun, and you can also get vitamin D through your diet, from foods like fatty fish, eggs, cheese, beef liver, and mushrooms.
“Vitamin D helps your body absorb calcium more efficiently,” explains Brynna Connor, MD, a board-certified family medicine physician specializing in anti-aging and regenerative medicine and the Healthcare Ambassador for NorthWestPharmacy.com.
“Only 15 to 20 percent of the calcium you ingest through eating and drinking is absorbed by the body, and vitamin D helps make that process more efficient. When vitamin D becomes activated, it forms the hormone calcitriol that interacts with cells in the kidneys and intestines, triggering the organs to absorb more calcium,” she explains.
Vitamin D can also have a range of other biological effects. “In addition to aiding in calcium absorption, vitamin D also helps to regulate calcium levels within the body to maintain the amount needed for normal bone mineralization and to avoid muscle spasms. Vitamin D also assists with respiratory function and immunity,” Connor says.
RELATED: 7 Calcium Deficiency Symptoms, According to Doctors.
Here’s How a Vitamin D Deficiency Impacts Your Health
Not getting enough vitamin D through sunlight, diet, or supplementation can have an impact on your bone health and your overall health.
“Not getting enough vitamin D can, over time, lead to serious bone conditions like rickets in kids and soft bones in adults. It’s also linked to other serious health issues, including heart disease, certain cancers, and high blood pressure,” says Chris Mohr, Phd, RD, a fitness and nutrition advisor at Fortune Recommends Health.
The Cleveland Clinic adds that in cases of chronic or severe vitamin D deficiency, a decline in calcium and phosphorus absorption by your intestines can lead to hypocalcemia, or low calcium levels in your blood. “This leads to secondary hyperparathyroidism (overactive parathyroid glands attempting to keep blood calcium levels normal),” they note.
16 Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms to Watch Out For
The symptoms of a vitamin D deficiency are non-specific, meaning they can have a range of underlying causes. But most people who have a vitamin D deficiency have no underlying causes. They simply aren’t getting enough through direct sun exposure, diet, or supplementation.
However, some people will develop a vitamin D deficiency due to another underlying condition. This can include malnutrition, kidney or liver failure, cystic fibrosis, certain types of cancer such as lymphoma, gastrointestinal conditions including Crohn’s disease and celiac disease, and more. Certain medications can also cause vitamin D deficiency as a side effect.
However, if you notice several symptoms associated with low vitamin D, this is a good cause to request a blood test to check your levels.
“Symptoms will vary from person to person, which is why you should consult a physician if you begin experiencing one or more of these symptoms or if they suddenly become worse,” notes Connor.
RELATED: 5 Supplements That Can Damage Your Kidneys, Doctors Say.
1. Fatigue

If you tend to feel especially sluggish when you spend less time outdoors, this could indicate that you’re running low on vitamin D. In fact, according to a 2015 study published in the Global Journal of Health Science, 89 percent of participants who reported frequent fatigue had inadequate vitamin D levels.
“Low levels of vitamin D can lead to feelings of fatigue because vitamin D is involved in energy production,” explains Mohr. “Its deficiency can impact the efficiency of mitochondria, leading to decreased energy production. Restoring vitamin D levels can improve mitochondrial function, helping to reduce fatigue caused by low levels.”
2. Bone pain

Vitamin D is essential to your bone health, so it should come as no surprise to learn that, according to a 2009 study published in the journal American Family Physician, aches and painful tenderness in your bones could be due to a vitamin D deficiency—especially if you feel discomfort when you put pressure over your breastbone or shinbone areas.
The study notes that this often gets misdiagnosed as fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome, or arthritis, so it’s important to discuss any pain with your doctor.
3. Lower back pain
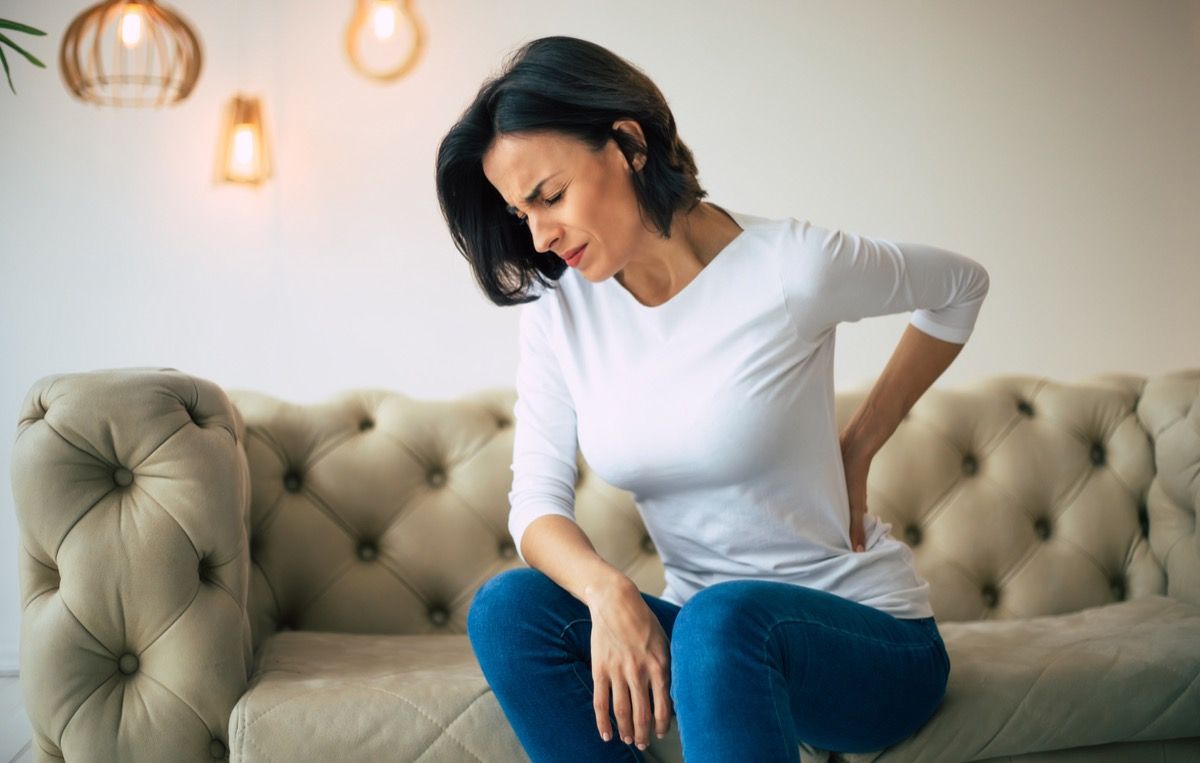

“Vitamin D promotes calcium absorption in the gut, which is important for maintaining strong bones,” explains Mohr. “Deficiency in vitamin D can lead to a decrease in calcium absorption, resulting in weaker bones and pain, particularly in the back.”
This is a symptom that women should especially watch out for. A 2008 study published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society concluded that lower concentrations of vitamin D were linked to significant back pain in women. However, the same connection was not found in men.
4. Muscle pain
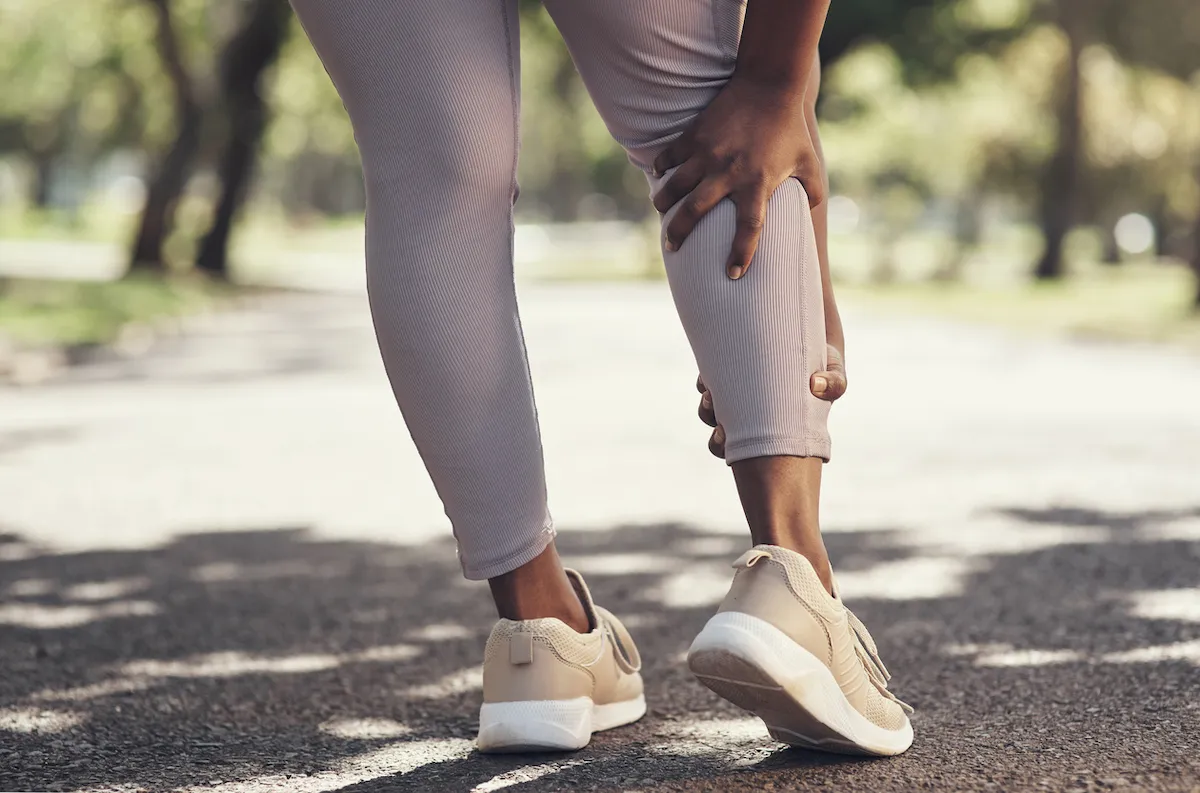

Mohr says this is a lesser-known symptom of a vitamin D deficiency: “With its anti-inflammatory properties, vitamin D helps to reduce inflammation often associated with muscle pain. Low levels may lead to increased muscle sensitivity and pain.”
RELATED: 12 Supplements You Should Never Take Together, Medical Experts Say.
5. Joint pain

There’s a long list of conditions responsible for joint issues, but this is one you don’t hear about very often.
“Low vitamin D levels in the blood cause an inflammatory response, causing pain and inflammation in the joints,” says Kelly Springer, MS, RD, founder of Kelly’s Choice.
To this point, a 2012 study published in the journal Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism found that “vitamin D deficiency is highly prevalent in patients with RA [rheumatoid arthritis], and that vitamin D deficiency may be linked to disease severity in RA.”
6. Tingling in the hands or feet
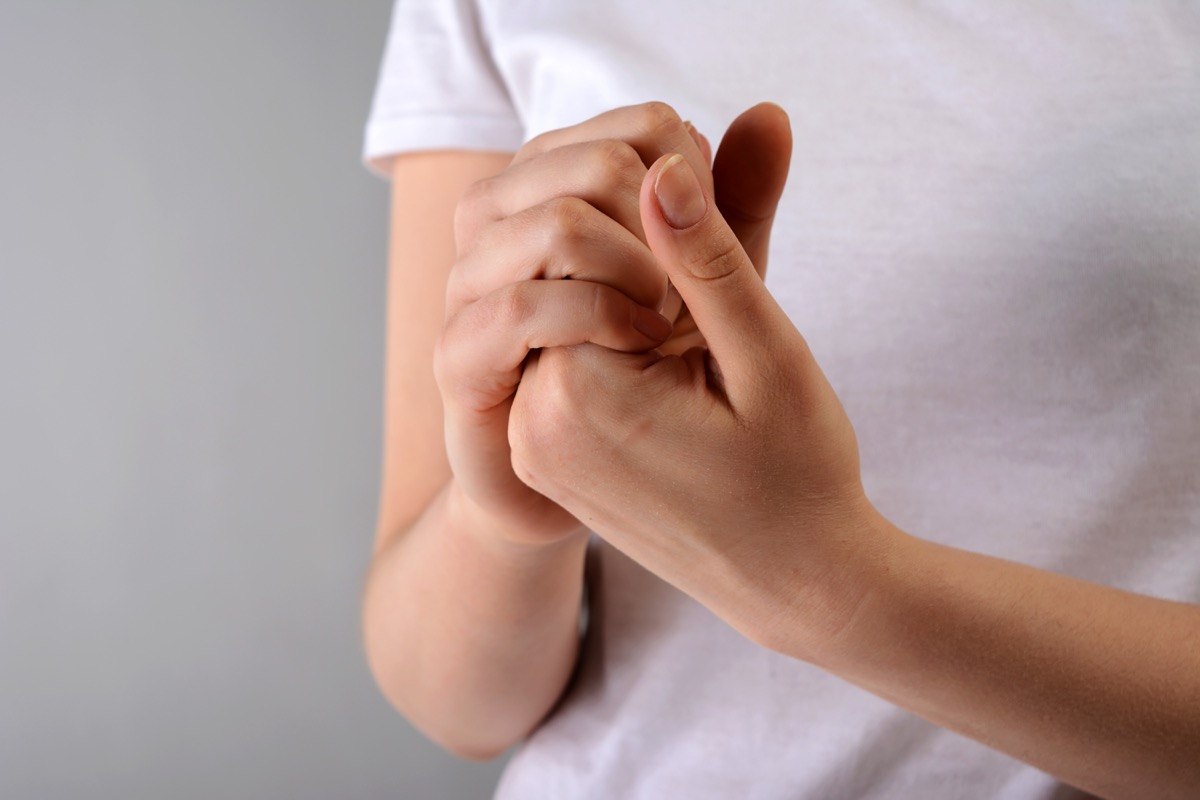

Connor points out that if you experience tingling or a pins-and-deeds feeling in your hands or feet, this could also be due to a vitamin D deficiency.
Vitamin D deficiency and the presence of this particular symptom are both more commonly experienced among people who also have Type 2 diabetes, according to a 2012 study published in the journal Diabetic Medicine.
“In the weighted population, 81 percent of adults with diabetes had vitamin D insufficiency,” the study authors wrote. “Within the three months preceding the questionnaire, 50 percent reported experiencing pain or numbness (paresthesia) in their hands or feet; 37 percent reported pain or tingling in hands or feet; and 38 percent reported numbness or loss of feeling in hands or feet.”
7. Depression

The cold, sunless winter months definitely aren’t good for your vitamin D levels—and that’s bad news for your mood.
“With a vitamin D deficiency, an individual is more likely to experience depression since vitamin D receptors help regulate mood,” says Springer.
And there’s science to back that up. According to an extensive 2018 meta-analysis published in The British Journal of Psychiatry that looked at 31,424 participants, low levels of vitamin D are, in fact, associated with depression.
8. Trouble sleeping
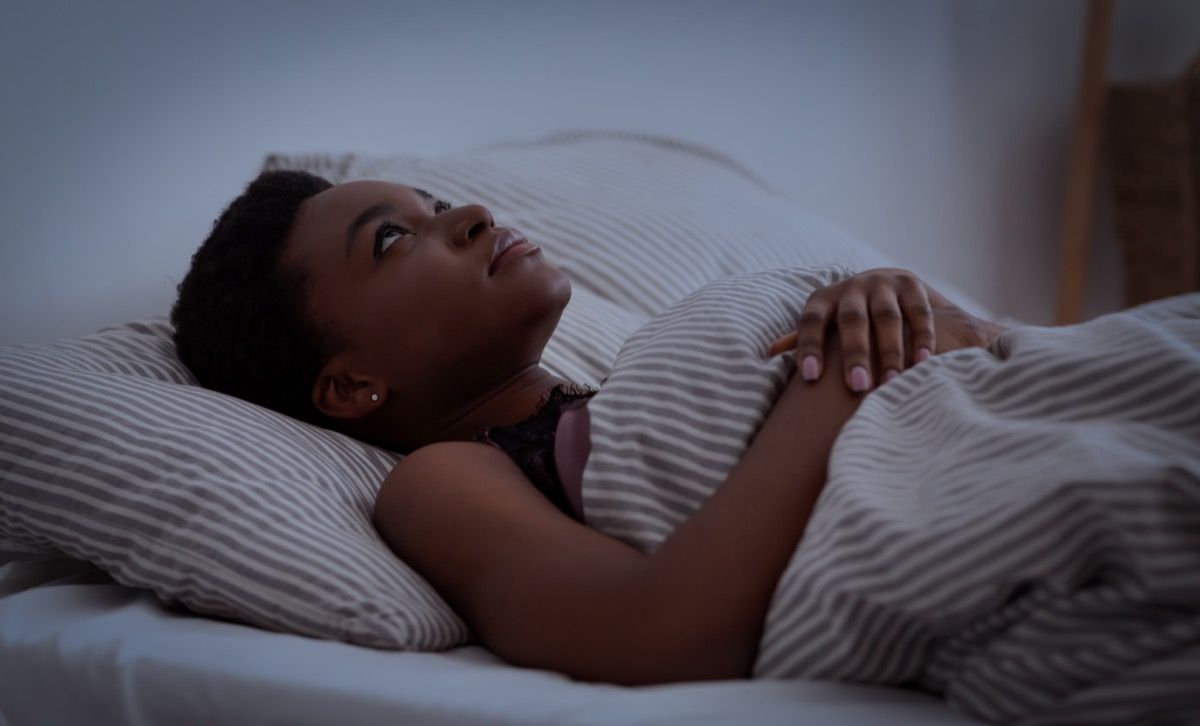

A 2018 meta-analysis of 9,397 subjects published in the journal Nutrients concluded that vitamin D deficiency is associated with a higher risk of sleep disorders, as well as poor sleep quality, short sleep duration, and sleepiness.
Moreover, a 2022 meta-analysis found that vitamin D supplementation “is promising in improving sleep quality.”
RELATED: 5 Supplements That Can Damage Your Kidneys, Doctors Say.
9. Hair loss

Michael May, MD, medical director at Wimpole Clinic, previously told Best Life that vitamin D is essential in cell regulation and the immune system. Therefore, a deficiency could cause hair loss.
To his point, a 2013 study published in the journal Skin Pharmacology and Physiology showed that women with hair loss had much lower levels of vitamin D than those who weren’t losing their hair.
10. Eczema

If you have atopic dermatitis—a common type of eczema that causes red and itchy skin—it’s a good idea to have your doctor check for a vitamin D deficiency.
A 2011 study published in the British Journal of Dermatology found that children with low levels of the vitamin tended to have more severe symptoms of the skin issue.
In addition to regulating the immune system, the National Eczema Association (NEA) explains that vitamin D can “suppress overall inflammation, promote a stronger skin barrier, and lessen the severity of eczema symptoms.”
Peter Lio, assistant professor of clinical dermatology and pediatrics at Northwestern University’s Feinberg School of Medicine and the founding director of the Chicago Integrative Eczema Center, told the NEA, “I recommend vitamin D supplementation to my eczema patients. While I do not think that all of them are necessarily deficient, I do think that many of my patients, if not most, have a relative vitamin D insufficiency.”
11. Getting sick more than normal

Do you feel like you’re constantly getting sick? Well, that could be due to a vitamin D deficiency, according to a 2010 study published in the journal Molecular Nutrition and Food Research. Researchers found that vitamin D directly connects to how your immune system responds to various infections and viruses.
On top of that, a 2021 study published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that “the habitual use of vitamin D supplements was significantly associated with a 34% lower risk of COVID-19 infection.”
12. Digestive problems

Living with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) means dealing with inflammation of your digestive tract, which results in diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fatigue. However, getting the right amount of vitamin D can lower your risk of having to deal with such a difficult condition.
That’s because, according to a 2013 study published in the journal Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, being vitamin D deficient might not only increase your risk of developing IBD but also factor into its severity.
A separate study published in the journal Nutrients in 2019 explained that vitamin D supplementation “has been shown to regulate gastrointestinal microbiota function, and promote anti-inflammatory, tolerogenic immune responses” in those with IBD.
RELATED: 8 Signs You’re Not Getting Enough Iron, Doctors Say.
13. Dizziness

When you have benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), you experience episodes of dizziness and may feel like you’re spinning—and that could all come down to your vitamin D levels.
According to a 2018 study published in the European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology, not getting an adequate amount of vitamin D can cause the disorder to develop and—if you don’t up your intake—persist.
14. Erectile Dysfunction

There are many factors that contribute to erectile dysfunction (ED)—alcohol, smoking, high blood pressure, and diabetes, to name a few. But, according to 2015 research conducted by Johns Hopkins University, vitamin D can be a direct cause as well.
The research found that men who were vitamin D deficient were 32 percent more likely to have ED than men with normal levels of the sunshine vitamin.
15. Frequent UTIs

No one wants to deal with a urinary tract infection (UTI). You likely know that the issue is typically caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract and multiplying. But were you aware that having low levels of vitamin D could be the reason behind the infection, too?
According to a 2020 study published in the Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, women of reproductive age with low vitamin D levels are more susceptible to UTIs.
16. Severe PMS symptoms

UTIs aren’t the only problem women face when they have a vitamin D deficiency. In an article on his website, Julian Whitaker, MD, said severe PMS symptoms—like mood swings, food cravings, and tender breasts—could be the result of not having enough vitamin D in your body.
He pointed out that past research showed those women who upped their vitamin D intake had a 40 percent lower risk of developing those sometimes-unbearable aches and pains than those who didn’t.
RELATED: 9 Supplements That Can Damage Your Stomach, Doctors Say.
How to Safely Raise Your Vitamin D Levels
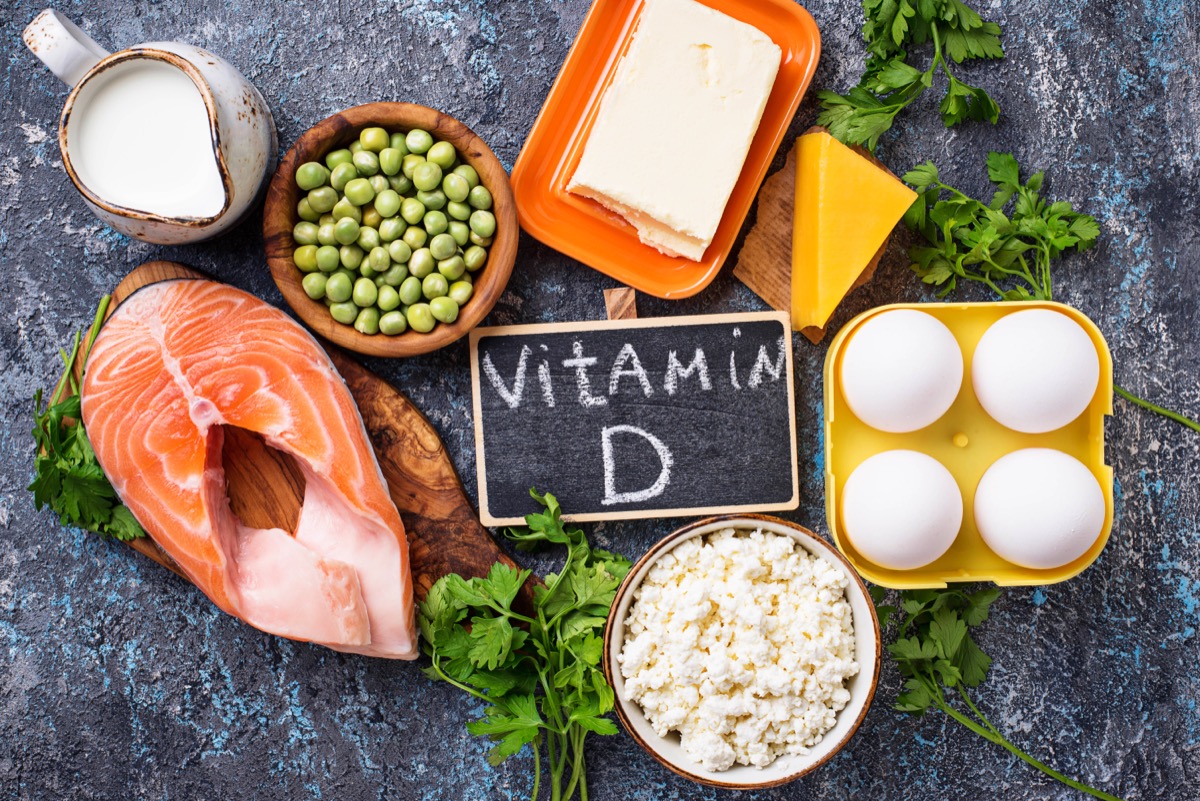

If your doctor performs a blood test and confirms that you do in fact have a vitamin D deficiency, they’ll want to treat any underlying causes while also bringing your levels up.
“The safest way to raise your levels is to eat a diet rich in vitamin D,” says Connor. “You can also take vitamin D supplements to help raise your vitamin D levels and improve your body’s calcium absorption.”
In June 2024, the Endocrine Society updated its guidelines for how much vitamin D people should get daily. Healthy adults between the ages of 19 and 75 should continue adhering to the Institutes of Medicine’s (IOM) recommendation of 600 international units (IU) of vitamin D. For adults over age 75, as well as adults with high-risk prediabetes, children, and pregnant people, the Endocrine Society now recommends extra vitamin D, depending on which group someone falls into.
“As with any supplement, you should talk to your doctor before starting a new course of treatment to ensure there is no risk of adverse events,” Connor says.
Best Life offers the most up-to-date information from top experts, new research, and health agencies, but our content is not meant to be a substitute for professional guidance. When it comes to the medication you’re taking or any other health questions you have, always consult your healthcare provider directly.
This story has been updated to include additional entries, fact-checking, and copy-editing.
- Source: Cleveland Clinic: Vitamin D Deficiency
- Source: The American Journal of Geriatric Pharmacotherapy: Prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency in elderly ambulatory outpatients in Denver, Colorado
- Source: Global Journal of Health Science: Fatigue and Vitamin D Status in Iranian Female Nurses
- Source: American Family Physician: Recognition and Management of Vitamin D Deficiency
- Source: Journal of the American Geriatrics Society: Associations Between Vitamin D Status and Pain in Older Adults: The Invecchiare in Chianti Study
- Source: Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism: Vitamin D and rheumatoid arthritis
- Source: Diabetic Medicine: Association between vitamin D and diabetic neuropathy in a nationally representative sample
- Source: Nutrients: The Association between Vitamin D Deficiency and Sleep Disorders
- Source: Nutrients: Vitamin D Supplementation and Sleep
- Source: Skin Pharmacology and Physiology: Serum Ferritin and Vitamin D in Female Hair Loss: Do They Play a Role?
- Source: British Journal of Dermatology: Correlation between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and severity of atopic dermatitis in children
- Source: National Eczema Association: Get the Facts: Vitamin D
- Source: Molecular Nutrition and Food Research: A review of the critical role of vitamin D in the functioning of the immune system and the clinical implications of vitamin D deficiency
- Source: The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition: Habitual use of vitamin D supplements and risk of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection
- Source: Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics: Review article: vitamin D and inflammatory bowel diseases
- Source: Nutrients: The Role of Vitamin D in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Source: European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology: Association of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo with vitamin D deficiency
- Source: Johns Hopkins University: Vitamin D deficiency is independently associated with greater prevalence of erectile dysfunction
- Source: Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences: Vitamin D deficiency as a risk factor for urinary tract infection in women at reproductive age
- Source: Archives of Internal Medicine: Calcium and vitamin D intake and risk of incident premenstrual syndrome
- Source: Endocrine Society: Vitamin D for the Prevention of Disease Guideline Resources