4 Common Medications That Cause Hair Loss, According to a Pharmacist

It’s not unusual to find stray hairs in the shower or sink after you complete your daily bathroom routine: The American Academy of Dermatology Association reports that shedding between 50 to 100 hairs daily is normal. But if you find yourself losing more hair than you’d care to admit, it could be due to a medication you’re taking. Though hair loss is a relatively rare side effect, some drugs can cause excessive hair loss by interfering with your scalp’s normal hair growth cycle. Read on to learn from a pharmacist which common medications could be triggering your hair loss—and what you can do to stop it.
READ THIS NEXT: This Is Why You’re Suddenly Losing More Hair, Doctors Say.
1
Beta-blockers
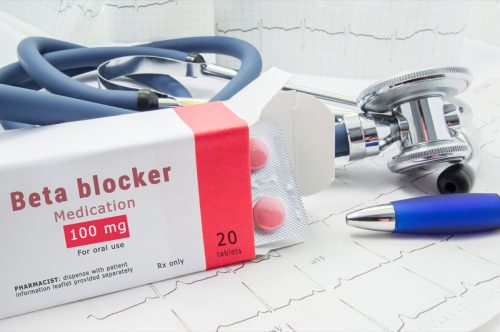
Beta-blockers are a class of drugs commonly prescribed to treat heart-related conditions such as high blood pressure. They include drugs such as propranolol (Inderal), atenolol (Tenormin), bisoprolol (Zebeta), and metoprolol (Lopressor). Many beta-blocker users report side effects such as exhaustion and drowsiness, but another less common symptom is hair loss. Brandi Cole, PharmD, pharmacist and nutritionist at Persona Nutrition, tells Best Life, “Beta-blockers change your body’s response to stress hormones, like adrenaline, to lower your heart rate and reduce blood pressure. These changes are thought to impact hair growth at the follicle and may stop new hairs from growing.”
The good news is that hair loss from beta-blockers such as propranolol isn’t permanent, and the symptom stops once you stop taking the medication. If you’re concerned about hair loss associated with your beta-blockers, talk to your healthcare provider about taking a lower dose and upping your dosage gradually.
READ THIS NEXT:Never Take These Common Medications With Your Morning Coffee, Pharmacists Say.
2
Seizure medications
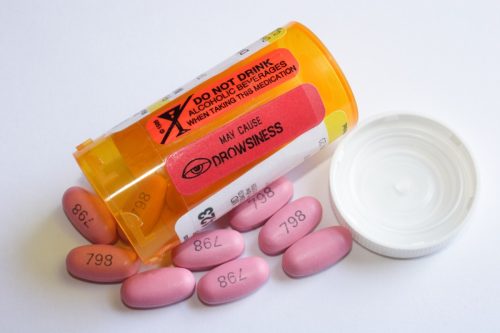
“Seizure medications are linked with hair loss related to nutrient deficiencies,” Cole says. “Depakote, used in treating both seizure and several mood disorders, is the most likely offender. Supplementing with a multivitamin containing plenty of hair-healthy B vitamins might help prevent or lessen hair loss associated with certain seizure medications.”
A systematic review of 127 studies published in Seizure in 2021 found that anti-seizure medications may be associated with various adverse cosmetic effects, most notably hair loss, acne, and hirsutism—a condition characterized by excessive body hair growth.
3
NSAIDs

Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are the most commonly prescribed medications for treating chronic pain conditions such as arthritis, says the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS). You’re likely familiar with the over-the-counter (OTC) NSAIDs aspirin and ibuprofen (both widely used for pain relief), but many NSAIDs require a prescription. These include celecoxib (Celebrex), diclofenac (Voltaren), and fenoprofen (Nalfon). Unfortunately, each NSAID has its own set of side effects. Common symptoms include stomach and gastrointestinal upset, elevated blood pressure, and kidney issues.
A lesser-known side effect of NSAIDs is hair loss. “Drugs to treat everyday aches and pains by reducing inflammation are available by prescription and OTC, both of which can contribute to hair loss,” says Cole. “NSAIDs can cause hair follicles to enter their resting phase too soon, stunting hair growth. To minimize the risk of hair loss, limit your NSAIDs and only use them as needed.”
For more health advice delivered straight to your inbox, sign up for our daily newsletter.
4
Antidepressants

“Scientists aren’t sure why certain antidepressants cause hair loss, but we do know that some antidepressants are more closely linked to this side effect than others,” explains Cole. “The antidepressant Bupropion seems to pose the biggest risk for hair loss, while Paroxetine poses the smallest risk. So if you’re experiencing hair loss, changing your antidepressant might be the answer.” While antidepressant-induced hair loss is rare, it’s a side effect associated with nearly every antidepressant, according to a 2018 study published in International Clinical Psychopharmacology.
Speak with your doctor if you’re experiencing hair loss.
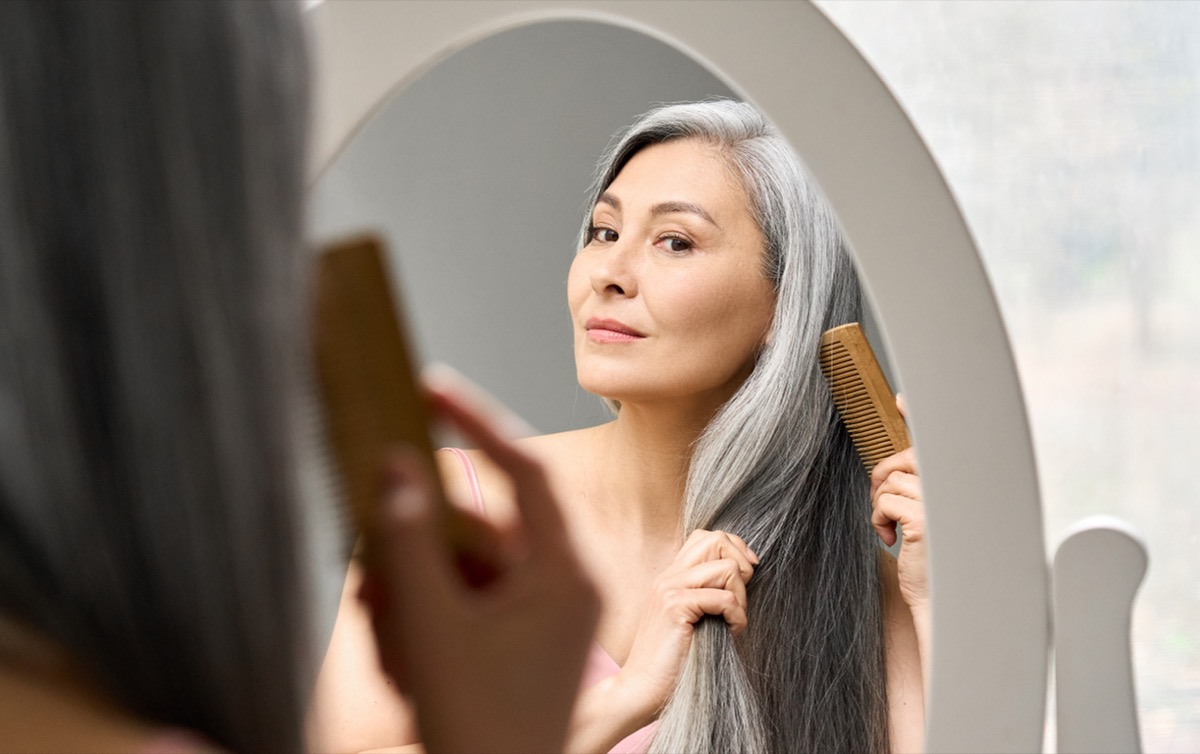

Ultimately, hair loss can be caused by many different factors. The best way to determine if your medication is causing your hair loss is to stop taking it and see if symptoms dissipate. Always speak with your doctor before stopping or altering your medication intake. In addition, Cole advises supporting healthy hair growth with proper nutrition.
“Patients with certain vitamin deficiencies are more likely to experience hair loss,” she says. “Low levels of zinc, biotin, and vitamin D are associated with hair loss, so finding a great multivitamin containing these three key nutrients can help. Additionally, a diet rich in omega-3s and antioxidants can support healthy hair follicles.”
Best Life offers the most up-to-date information from top experts, new research, and health agencies, but our content is not meant to be a substitute for professional guidance. Always consult your healthcare provider directly when it comes to the medication you’re taking or any other health questions you have.